Publication Date:
2007-05-23
Institutions involved:
- Fundamental Research Laboratory, Asahi Breweries, Ltd. (1-21, Midori 1-chome, Moriya-shi, Ibaraki 302-0106, JAPAN)
- Department of Health and Nutrition, University of Arts and Sciences (1288, Komagome, Iwatsuki-ku, Saitama-shi, Saitama 339-8539, JAPAN)
- Department of Biology, Ochanomizu University (2-1-1 Ohtsuka, Bunkyo-ku, Tokyo 112-8610, JAPAN)
Participants:
71 moderately obese adults, male and female, considered healthy but at risk due to elevated BMI (23-30)
Duration:
12 weeks
Dosage:
Apple polyphenols 600mg/day
Learn more
Try Apple Poly Now
Key Takeaways:
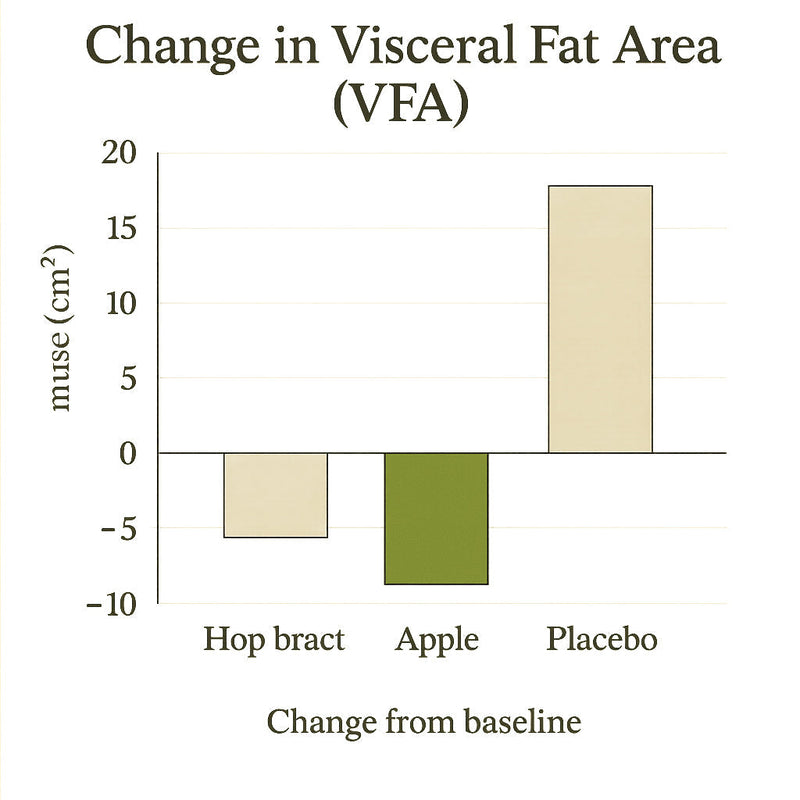
CT scans documented reductions in visceral and total fat area, even at modest dose of 600 mg/day. Apple polyphenols proved superior to hop bract polyphenols and placebo.
Apple polyphenols (600 mg/day) significantly reduced total and LDL cholesterol over a 12-week intake period in adults with BMI 23–30.
Growing evidence suggests that apple polyphenols offer a safe and effective approach to managing early metabolic risk— without requiring major diet or lifestyle changes.
Apple Poly Summary:
Why is this study important? This randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial investigated the effects of apple polyphenol supplementation on cholesterol metabolism in adults with elevated BMI. After 12 weeks, participants taking apple polyphenols showed significant reductions in total and LDL cholesterol, along with improvements in visceral fat and adiponectin levels—highlighting their potential as a safe, food-based intervention for cardiometabolic health.
In Plain English: This study tested whether apple polyphenol capsules could help people with higher body weight improve their cholesterol. After three months, those who took the supplement had lower levels of “bad” cholesterol and less belly fat, without any side effects. It suggests that apples might help support heart health from the inside out.
For Medical Professionals: In this 12-week RCT involving 71 moderately obese Japanese adults (BMI 23–30), participants received 600 mg/day of polyphenols extracted from apples or hop bract. The apple polyphenol group showed statistically significant reductions in total cholesterol and LDL-C compared to placebo, with greater efficacy than the hop bract group. Visceral fat area decreased, and adiponectin levels improved. No adverse effects were reported. These findings support the lipid-lowering and adipokine-modulating potential of apple polyphenols in overweight populations.
Abstract:
We performed a randomized double-blind, placebo-controlled study on moderately obese male and female subjects (71 subjects) with a body mass index ranging from 23 to 30 to evaluate the efficacy of 12-week intake of polyphenols extracted from apples and hop bract (600 mg/day). We confirmed that 12-week ingestion of polyphenol-containing capsules significantly decreased total cholesterol and LDL cholesterol levels.
The effects of the apple polyphenol-containing capsules were more marked than those of the hop bract polyphenol-containing capsules. The visceral fat area and the level of adiponectin in the group administered apple polyphenols improved in comparison with the control group.
Blood and physical examinations revealed (no) clinical problems, and no adverse reactions were observed during the ingestion period.
These results demonstrate that apple polyphenols regulate fat metabolism in healthy subjects with relatively high body mass index.
Key words: apple polyphenols, total cholesterol, LDL-cholesterol, body mass index, visceral fat, adiponectin
J. Oleo Sci. 56, (8) 417-428 (2007) DOI: 10.5650/jos.56.417